Murata will provide a complete solution for USB noise reduction measures and verification from the following six aspects. 1. A brief history of USB. What noise issues may occur with USB4. 3. Noise reduction: How to apply CMCC is crucial (recommended CMCC products from Murata: NFG0QHB372HS2/NFG0QHB542HS2). 4. Evaluation of radiated noise. 5. Internal EMC assessment and response measures. 6. Signal integrity confirmation.
1. Brief History of USB4
As a differential interface standard mainly used for transmitting data between host devices such as computers and device devices, USB (Universal Serial Bus) has been widely popularized. With the increasing demand in the market for high-capacity data transmission in high-speed communication and the integration of multiple differential interface standards, USB4 was designated as a new standard in September 2019, mainly focusing on computers and their peripheral devices, and further popularized.
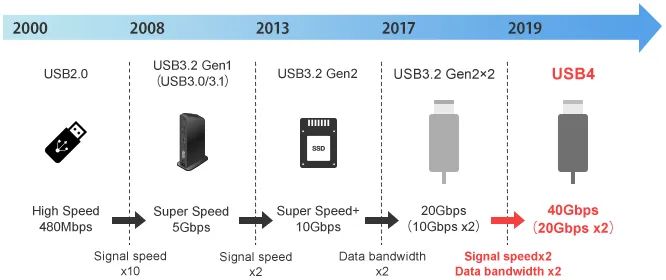
The evolution of USB interfaces
We know that before USB4, several USB connector standards had already been unified as Type-C connector (USB3.2) - the trend of using one Type-C cable to be compatible with various interfaces. In a laptop PC, charging, video transmission, and data transmission can be achieved with just one cable.
So, why did it evolve to USB4 again?
The driving force of the mandatory law released by the European Commission to unify charging standards into Type-C has made Type-C connectors a de facto standard, thus integrating Thunderbolt with USB! (See figure below)
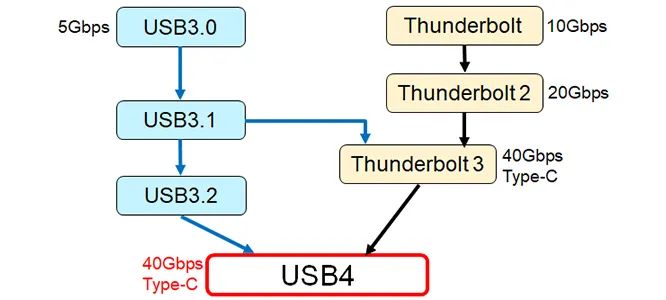
USB4: The integration of Thunderbolt and USB interface results
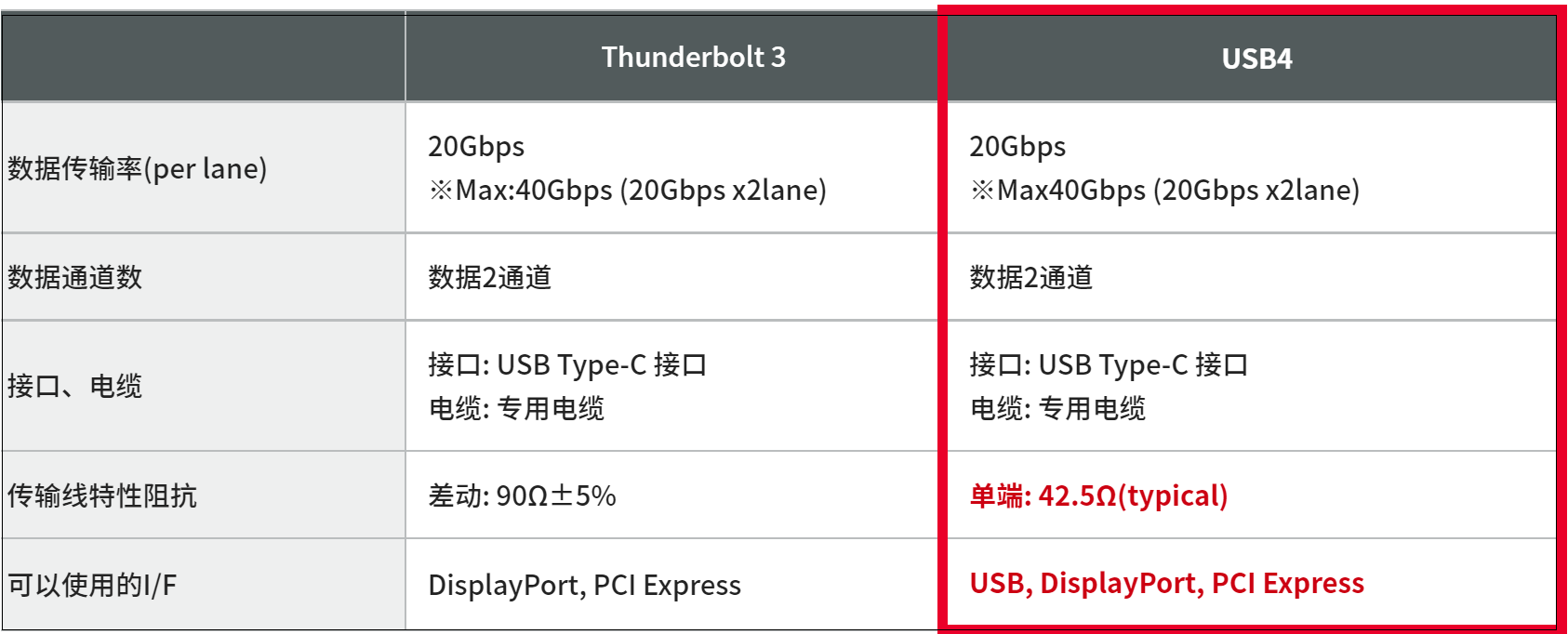
Thunderbolt 3 adopts a USB Type-C interface, so the ports of Thunderbolt 3 can also be used as USB 3.1 ports. The USB4 standard is fully compatible with Thunderbolt 3. Most of the electrical performance parameters of USB4 are based on Thunderbolt 3.
USB4 has the same fastest data transfer speed as Thunderbolt 3. It is not difficult to see that the USB4 standard will greatly improve the user experience of end users in the future.
What noise issues may occur with USB4
USB4, like Thunderbolt 3, has faster data transfer speed. Although there are slight differences in signal amplitude between the two, their basic specifications are the same (as shown in the figure below).
Therefore, like Thunderbolt 3, corresponding measures need to be taken for USB4 in terms of noise issues and signal integrity caused by data signals.
Specifically, when communicating with USB4, there are two types of noise issues that need to be addressed:
The radiation noise emitted by substrates and cables to the outside world, which affects the outside world;
Internal system EMC noise that causes interference with other circuits inside the device, leading to erroneous operations or reduced performance.
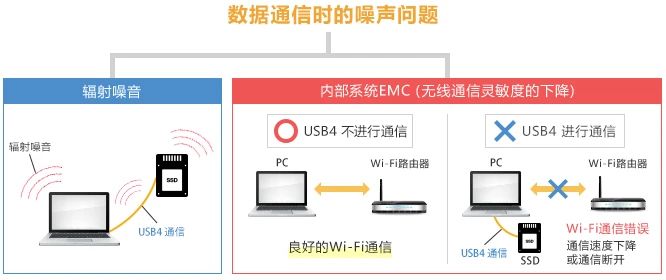
Noise issues during USB4 communication
Key points:
When communicating with USB4, noise may radiate from USB4 equipment or cables;
When USB4 communicates, the noise generated by the data signal interferes with the Wi Fi antenna inside the device, thereby reducing the sensitivity of Wi Fi communication, which is an EMC issue in the internal system.
It should be noted that during the verification testing period conducted in this article, there were no devices available on the market that could achieve USB4 communication (as of February 2020). Therefore, the following results are all noise evaluations of devices that can communicate using Thunderbolt 3, which has electrical performance parameters that are basically the same as USB4.
3. Noise reduction: How to apply CMCC is key
The following three measures are crucial for noise reduction during USB4 communication:
Install a common mode choke (CMCC) on the differential transmission line between the Host and Device devices
Install CMCC near the IC
Install CMCC that can prevent wire radiation
In the combination of Host and Device devices that can communicate with USB4, USB3.1 Gen2, PCI Express, and DisplayPort (as shown in the figure below), when using a common mode choke (CMCC) for noise reduction, where should it be installed (installation location) be considered? Product specifications? How to test and verify? Wait for the question. Below, the editor will explain one by one for you.
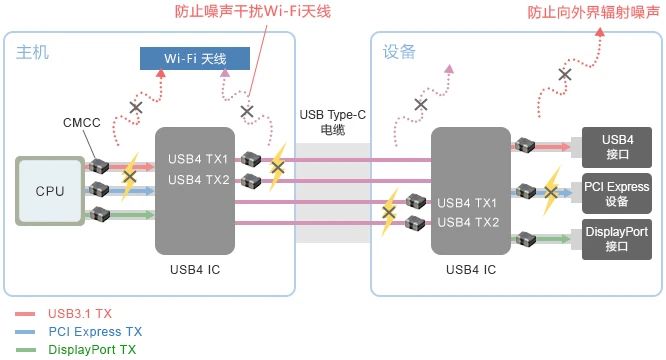
Example of USB4 noise reduction measures
Recommended by Murata : CMCC


4. Evaluation of radiated noise
In order to simulate the operation status of USB4 communication inside the computer, we connected the docking station capable of Thunderbolt 3, DisplayPort, Ethernet, and USB communication to the computer, and measured the radiated noise level from a distance of 3 meters (as shown in the figure below).
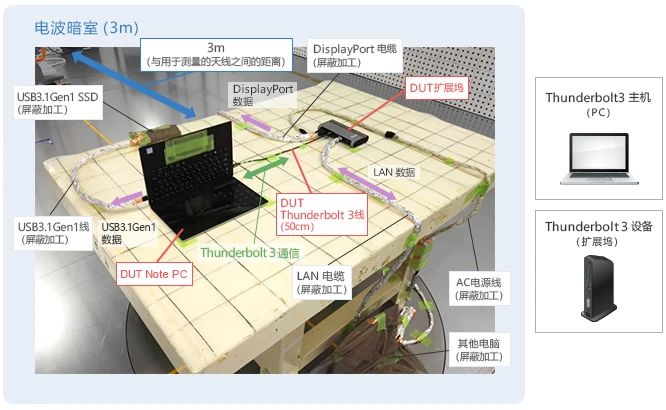
In order to eliminate noise outside of the Host and Device devices, we conducted shielding processing on the devices and their connecting cables.
The measurement results of radiated noise are shown in the following figure:
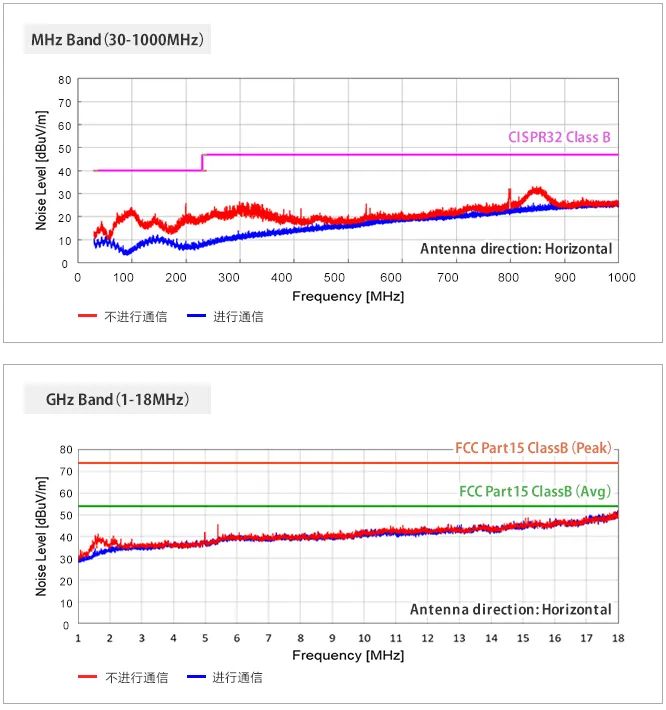
It can be seen that no noise exceeding the standard value was detected in the MHz and GHz frequency bands. Therefore, we can assume that USB4 can ensure a sufficient range of differences and there is a high likelihood that radiated noise will not cause problems.
6. Internal EMC assessment and response measures
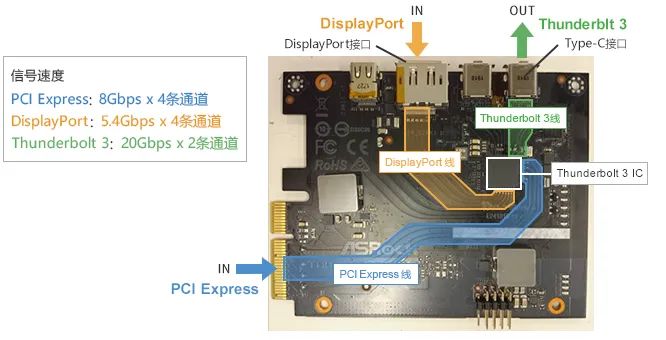
To investigate the impact of internal system EMC, we replaced USB4 with an expansion card that supports Thunderbolt 3 and evaluated the noise. Only ICs that support Thunderbolt 3 are installed in the expansion card (as shown in the figure below).
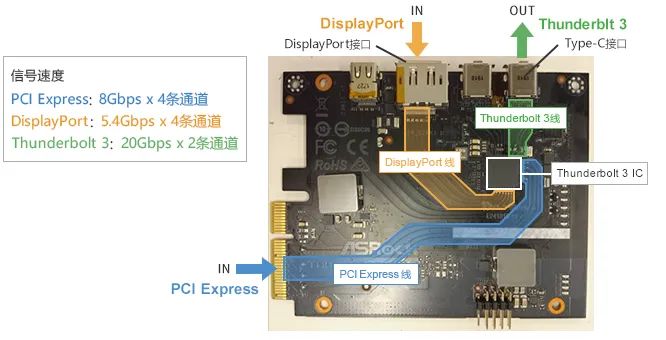
The structure of the expansion card is as follows: PCI Express signals (8Gbps x 4 channels) and DisplayPort signals (5.4Gbps x 4 channels) are input into the Thunderbolt 3 IC on the expansion card, which generates Thunderbolt 3 signals (20Gbps x 2 channels) and outputs them from the Type-C interface.
Evaluate the impact on Wi Fi reception sensitivity:
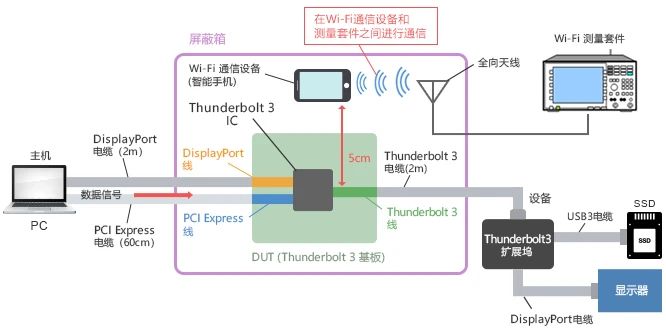
To confirm the impact of noise emitted by the substrate wires, we only placed the DUT in a shielding box and measured the Wi Fi reception sensitivity of nearby smartphones (as shown in the figure below).
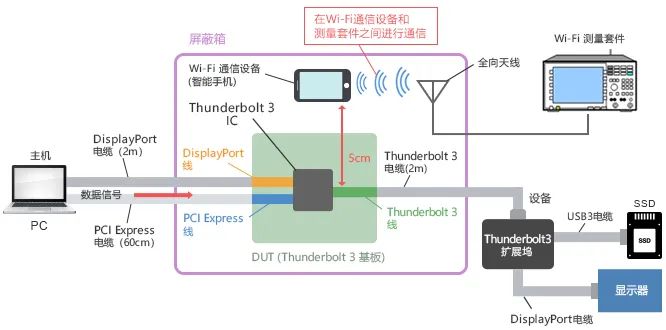
In future laptops that may install USB4, the installation location of Wi Fi antennas is showing a trend from the monitor to the motherboard, and the distance between the differential signal line and the antenna is expected to be shortened to 5 centimeters.
Therefore, in this evaluation, we also set the distance between the substrate wire and the smartphone to 5 centimeters. (Simulate the distance between the antenna and signal line inside a laptop)
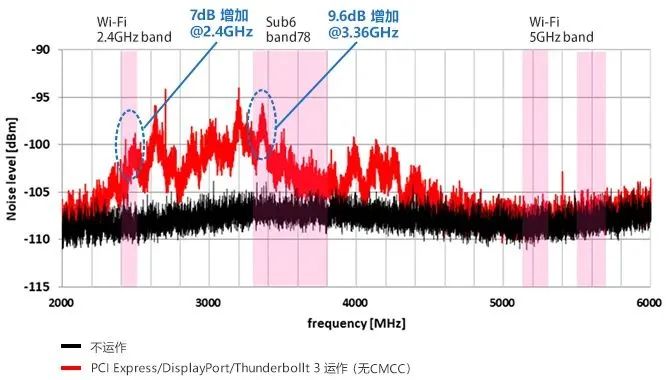
The following figure shows the measurement results of the EMC Wi Fi receiving sensitivity of the internal system when no measures are taken:
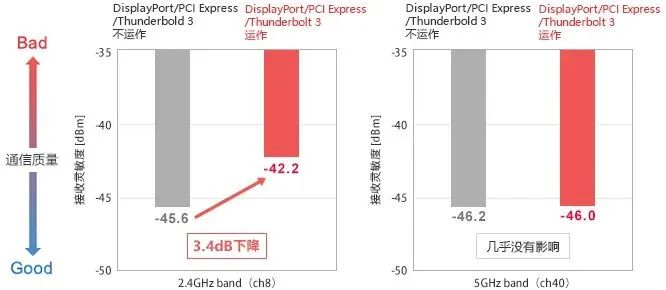
From the measurement results, it can be seen that the operation of USB4 has an impact on the sensitivity of Wi Fi reception: due to various data communications, the sensitivity of Wi Fi (2.4GHz frequency band) reception has decreased by about 3dB. This is likely the result of interference from the noise generated during communication to the antenna.
In this evaluation, no decrease in receiving sensitivity of DUT in the 5GHz frequency band was detected.
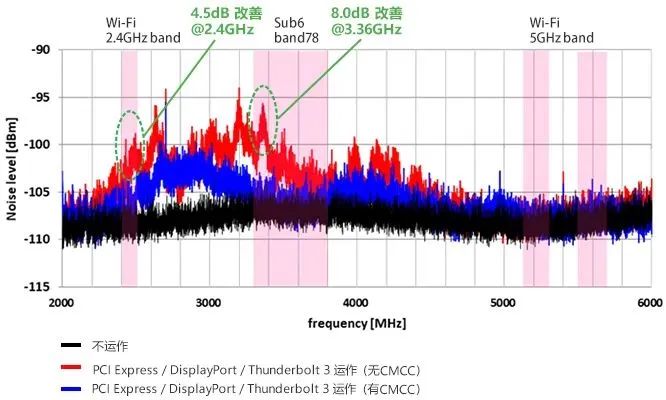
After taking noise reduction measures, the measurement results of receiving sensitivity are as follows:
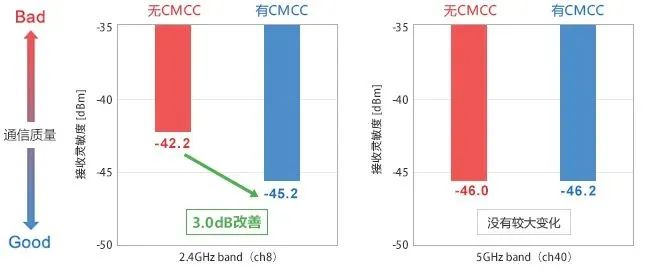
After taking noise reduction measures
It can be seen that when communicating with PCI Express, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt 3, by installing CMCC (NFG0QHB372) on each signal line, the receiving sensitivity of Wi Fi (2.4GHz) has increased by 3.0dB compared to before installing CMCC.
Key point: When communicating with Thunderbolt 3, the signal lines of PCI Express, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt 3 will emit broadband noise, leading to a decrease in wireless communication sensitivity. Inserting noise cancelling components at these locations (as shown in the figure below) is crucial for internal system EMC:
In order to reduce the noise emitted by wires, we installed CMCC (NFG0QHB372) on the transmission path of the noise, which is the signal line.
Evaluate the noise coupled with the antenna:
Next, we measured the noise level coupled with nearby antennas.
In this evaluation, the distance between the differential signal line and the antenna is also about 5 centimeters. The host uses a Thunderbolt 3 expansion card, while the device uses a Thunderbolt 3 docking station. Place an omnidirectional antenna 5 centimeters away from the Thunderbolt 3 signal line on the expansion card substrate and detect the noise radiated from the expansion card substrate through this omnidirectional antenna.
When conducting signal communication, PCI Express, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt 3 signals simultaneously pass through the expansion card.
The measurement results of noise coupled with the antenna without taking any measures are shown in the following figure:
It should be noted that in order to eliminate noise outside of the Host and Device devices, we have conducted shielding processing on the devices and their connecting cables.
After taking measures, the noise coupled with the antenna was reduced by a maximum of 8dB (as shown in the figure below).
It is important to consider the frequency of coupled noise and select components that can control noise in the 2.4GHz to 5GHz frequency band.
Measure nearby noise:
In order to identify the location of the noise generation, we also used an EMC measuring instrument that can map the near-field for measurement.
Due to various communications, broadband noise is transmitted on the TX signal lines of Thunderbolt 3, PCI Express Gen3, and DisplayPort on the expansion card substrate.
The measurement results without taking measures are shown in the following figure:
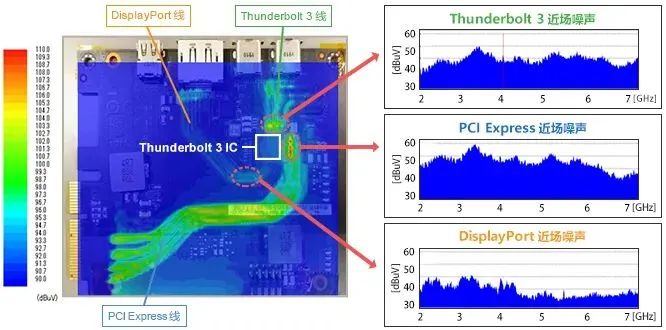
It can be inferred that these broadband noise radiated from the signal line to the external space and coupled with the wireless antenna. This reason leads to a decrease in Wi Fi reception sensitivity and Sub6 reception sensitivity.
We speculate that this phenomenon may also occur on USB4, which has electrical characteristic parameters similar to Thunderbolt 3.
Summary:
From the above evaluation, it can be understood that when Thunderbolt 3 communicates, the signal lines of PCI Express, DisplayPort, and Thunderbolt 3 will emit broadband noise, leading to a decrease in wireless communication sensitivity.
Installing CMCC (NFG0QHB372) on the signal line, which is the path of noise transmission, can effectively reduce the noise radiated by wires.
6. Signal integrity confirmation
Due to the use of a common mode choke on the signal line for noise reduction, we have also confirmed the impact on signal integrity. The signal for confirmation is Thunderbolt 3.
The eye diagram measurement settings for confirming the signal waveform are shown in the following figure:
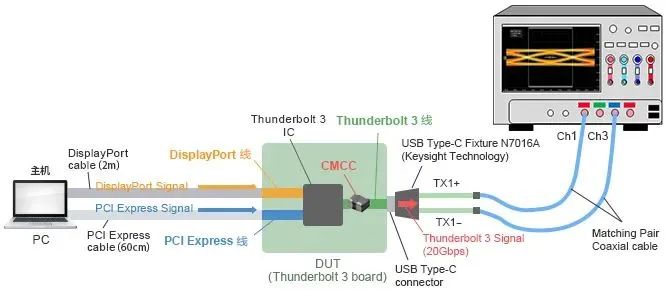
We have confirmed whether the use of a common mode choke will affect signal integrity by outputting Thunderbolt 3 test mode from the DUT. The results are as follows:
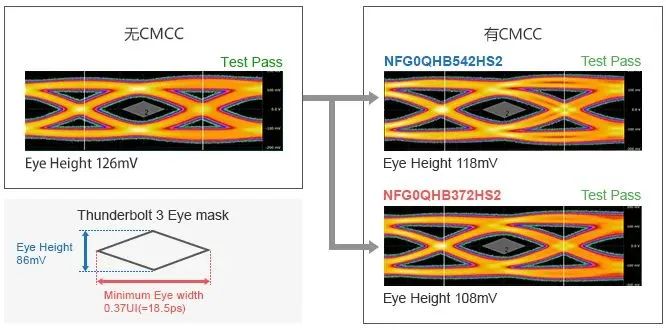
After using a common mode choke, the integrity of the signal waveform remains at the same level as before inserting the filter, and has passed the consistency test of Thunderbolt 3.
USB4 has the same signal speed (maximum of 20Gbps), so it should also be able to pass waveform testing.
Summary:
This article explores the corresponding measures that USB4 needs to take in terms of noise issues and signal integrity caused by data signals.
Radiated noise:
Simulated the operating environment of USB4 and evaluated the noise.
Radiation noise did not cause any problems in the frequency bands of 30-1000MHz and 1-18GHz.
Wi Fi reception sensitivity:
In the operation of PCI Express, DisplayPort 1.4, and Thunderbolt 3, the Wi Fi reception sensitivity will decrease. Especially during the operation of USB 3.1 Gen2, it can be measured that the substrate wires emit noise in the 2.4GHz frequency band.
It can be inferred that USB4 will also produce the same noise during operation. The use of common mode choke can improve the issue of decreased Wi Fi sensitivity.
By using the components recommended by Murata, noise reduction can be achieved without affecting signal integrity. The common mode choke recommended by Murata has a higher cutoff frequency and less impact on high-speed signals. The peak attenuation characteristic is high and has good noise reduction characteristics.